How Bad Is Alcohol For Your Body?
It’s not a question of if alcohol is bad for the body. The real question you should be asking is, “how bad” is alcohol for the body.
Across various mass media, there is a constant reminder that alcohol is bad. But the information hasn’t been specific enough. So in this article, we’ll do justice to the dangers of alcohol for the body.
You may not be an alcohol addict, but this doesn’t excuse you from the substance’s negative effects. As long as you drink alcohol frequently, there’s the risk of side effects.
Despite the adverse effects, many people still consume alcohol frequently. The motive for frequently consuming alcohol ranges from escaping terrible realities to fitting in and seeking relief from stress. However, are all these reasons enough justification for the imminent adverse effects of alcohol?
A few drinks occasionally may not do much damage, at least in the short term. However, with heavy drinking and binges comes potential damage.
Here, we’ll take a closer look at how bad alcohol is for your body. Keep reading to learn more.
What Happens When You Take Alcohol?
Your body doesn’t digest alcohol. When you drink alcohol, it instantly finds its way into your bloodstream. From the bloodstream, the alcohol diverges towards different parts of your body.
The first port of call for alcohol is the brain, followed by the kidney, lungs and liver. When alcohol reaches the liver, the organ tries to break it down. However, the breakdown of alcohol is a hassle for the liver and can lead to diseases.
Weight
If you’re lightweight, your bloodstream and tissue will absorb alcohol faster. Therefore, the effects of alcohol on your body can be stronger.
Age
Age is somewhat directly tied to weight. Younger people tend to be in lower-weight classes. Hence, young adults and children feel alcohol’s effect faster. Because young people and children have brains still in development, taking alcohol can lead to immense damage.
At old age, alcohol’s effects become more severe, even if your drinking volume remains constant. You’ll feel the effects more because your body system is unable to process alcohol as effectively.
At old age, alcohol consumption can lead to serious medical issues. Old age alcoholism leaves you super prone to:
- Stroke
- Cancer
- Dementia
- Heart disease
- Confusion
- Depression
Gender

Women are generally smaller in size and weight than men. Therefore, if you’re a woman, it’ll take your tissues less time to absorb alcohol.
Even if the man and woman are the same size and weight, an equal volume of alcohol affects women faster than men. Women’s bodies have more fat and less water compared to men.
Hence, alcohol will assume a higher concentration in women. Alcohol breakdown in the liver is also more sluggish in women, owing to fewer enzymes facilitating the breakdown.
Stomach
About 20% of the alcohol your body absorbs goes through your stomach. The remaining 80% goes in through the small intestine. Therefore, irrespective of how little drink you take, it most likely will stimulate your appetite. The stimulation results from the dynamics of your stomach juices. On the flip side, too much alcohol can dampen your appetite, leading to malnutrition over time.
Alcohol is bad for the body because it can cause ulcers. An ulcer, in this case, results from a mix of gastric juice and alcohol, which irritate the stomach lining.
Brain
Liquor affects the part of the brain that controls actions and impulses. When too much alcohol hits the body within a short period, the brain becomes dull. When alcohol takes over, you become incapable of making appropriate actions or rational decisions.
Beyond actions, alcohol can take over your mood, resulting in unnecessary aggression. The more alcohol that gets to your brain through the blood, the worse off you get.
The initial thrill from the first few drinks disappears. Slurring words, blurry vision and lack of coordination soon become the best you can do.
What alcohol does to you in these moments range from bad to dangerous and lethal! It takes a long time for the effects to wear off. In the morning after a drunk night, your blood still contains alcohol — sometimes in high concentration.
Kidney
The presence of alcohol in your kidney produces more urine. Hence, you’ll urinate more often and may suffer thirst and dehydration.
Bloodstream
The presence of alcohol in your bloodstream causes blood vessels to dilate. Owing to the widening of the blood vessels, you’ll blush more as more blood rushes to the skin.
Temporarily, you may feel warm, immediately followed by heat loss. As a result, your body temperature drops drastically. A drop in blood pressure can also follow the consumption of alcohol.
Empty or Full Stomach
When your stomach is empty, the alcohol you take travels directly to the bloodstream. However, if your stomach is full, the rate of alcohol absorption reduces.
The Short-Term Effects of Alcohol on your Body
How alcohol affects you in the short term depends on the factors above. Below, we take a look at what the short-term effects of alcohol are. Read through and see just how bad alcohol is bad for you.
Hangover

There is no specific metric to tell you when a hangover becomes a certainty after drinking. Your chance of suffering a hangover increases the more you drink. For some people, a hangover can happen after one bottle of beer. For some, a six-pack won’t faze them.
How your body breaks down alcohol determines how bad the hangover is. A hangover can have the following effects on your body:
- Incessant urination followed by dehydration
- The immune system’s inflammatory response
- Stomach lining irritation
- Blood sugar reduction
- Blood vessels’ expansion
A hangover will come with the following symptoms;
- Thirst
- Muscle ache
- Poor concentration
- Fatigue
- Trembling
- Poor sleeping patterns
- Diarrhea
- Dryness of the mouth and eyes
- High sensitivity to sound and light
- Anxiety, irritation and depression
- Rapid heart rate
- Blood pressure
- Nausea
- Weakness
- Headache
- Dizziness
A hangover doesn’t occur when your blood alcohol rises. Instead, it happens when the alcohol concentration in your body goes down to zero. That’s why you are more likely to experience a hangover the following day after a bungee. At worst, a hangover lasts for about 24 hours before disappearing.
The following factors can contribute to how terrible your hangovers get:
- Drinking on an empty stomach
- Using other substances with alcohol
- Not getting enough sleep post-drinking
- Getting drunk on rum, brandy or whiskey
It’s best to start an alcohol addiction program if you’re having too many hangovers. Incessant hangovers are a gateway to some of the long-term effects of drinking alcohol.
Related Article: How Much Does Alcohol Rehab Cost in Vancouver?
Alcohol Poisoning
In the short term, alcohol health risks include alcohol poisoning. Alcohol poisoning isn’t a problem that disappears with time — it’s an emergency. Hence, reach out to the nearest health facility once you notice any of the following:
- Confusion
- Seizures
- Hypothermia
- (low body temperature)
- Sluggish and irregular breathing
- Unconsciousness or inability to deliberately remain conscious
- Pale skin
A delay in getting medical treatment after noticing the symptoms above can lead to death. So no matter how ‘non-threatening’ the signs you see are, it’s best to reach out to healthcare services immediately.
Lowered Inhibitions
Whenever you take too much alcohol, your inhibitions lower, and you start to feel relaxed. But, in the long run, lowered inhibition resulting from alcohol is bad for your body.
You can engage in risky activities in these moments, which can be life-changing. For instance, driving under the influence of alcohol is a function of lowered inhibitions, and it can have severe consequences.
The Long Term Effects of Alcohol on Your Body
According to the World Health Organization, about 200 diseases and illnesses have alcohol as a contributing factor. Here is a comprehensive list of the long term damages that alcohol can cause:
Social Dysfunction
Heavy alcohol use draws you away from society. Heavy alcohol use – addiction – wants to keep you alone. You may want to hide away from people that force you to own up to the reality of the addiction. Also, due to aggressive tendencies, you won’t relate with friends and loved ones properly.
Diabetes
The pancreas makes insulin, and other chemicals, with which the intestine breaks food down. Alcohol hampers that process.
Alcohol’s presence in the body can stop the effective transport of insulin. Together with toxins from alcohol, insulin leads to pancreas inflammation and can cause severe damage. Once pancreas damage occurs, the body won’t make its insulin — a situation that precludes diabetes.
Liver Disease
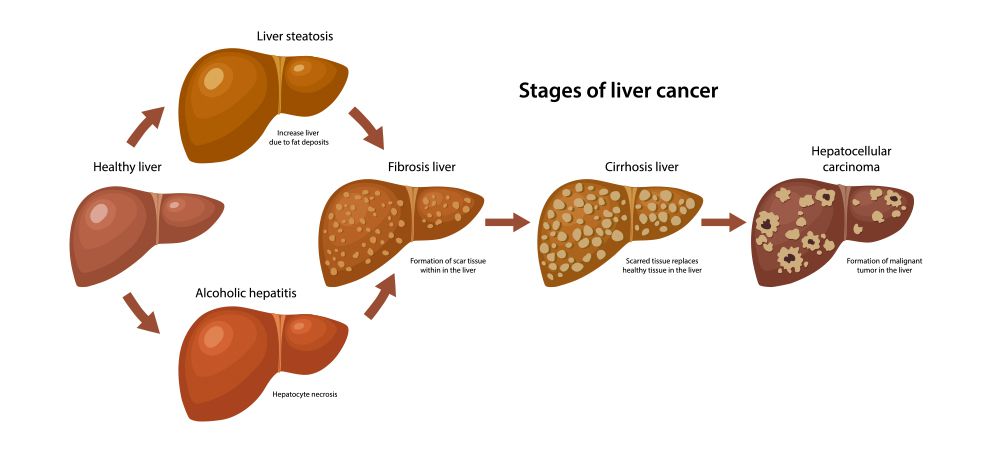
Both fat and fibrous tissues can impede blood flow. Essentially, your liver cells get starved of the nutrients they need for survival. The cells gradually die off, and after a while, the liver stops functioning.
Cancer
When you have diabetes, the whole situation can result in pancreatic cancer. Hence, you’ll need to invest heavily in health care.
Cognitive Impairment
If you drink heavily for an extended period, the shape and functioning of your brain can alter. The cells begin to change. Most times, the cells get smaller. Hence, alcohol shrinks your brain. The change in size and shape of the brain affects your thinking, memory and learning. Another side effect of brain shape damage is abnormal body temperature.
Other long term effects that can result from alcohol use include:
- Suicidal tendencies
- Addiction
- Mental health illnesses
- Risk to fetus
- Obesity
- Cardiovascular diseases
Frequently Asked Questions on Alcohol Consumption
Below we answer some of the common questions asked in relation to alcohol addiction:
 What does Binge Drinking Mean?
What does Binge Drinking Mean?
Binge drinking refers to the situation where you drink a lot of alcohol over a short time. Binge drinking happens because you’re trying to get intoxicated as fast as possible.
Hence, you’re open to the subsequent hangover, poisoning and other short-term effects. In the long term, binge drinking puts you in pole position to suffer from conditions like heart diseases, liver cirrhosis, diabetes and cancer.
How Much Alcohol is Bad for Your Health?
Going with the mantra that “too much alcohol is bad for your health” is the wrong approach. “Too much alcohol” is a metric that’s subjective at best. Hence, work with the thought that ‘even the smallest drop of alcohol is bad for your body.’ As much as you can, stay away from alcohol.
Final Take
There are no mincing words; alcohol is extremely bad for your body. Even in moderate amounts, over time, alcohol can cause permanent damage to your body. Hence, it’s best not to start drinking in the first place.
Even if you have a history or a present with alcohol, you don’t need to have a future with it. You can reach out to our alcohol addiction treatment service to prevent your abuse from getting worse.
Here at Inspire Change Wellness Centre, our addiction specialists can devise an alcohol treatment plan that works for you. Get in touch with us today!

 What does Binge Drinking Mean?
What does Binge Drinking Mean?